Decree 70/2025 is now effective, outlining 6 key compliance updates businesses must follow in accounting and reporting.
With Decree 70/2025 officially in effect, major regulatory changes are in place. These 6 key points are essential for every business to comply and avoid penalties in accounting operations.
- What is Decree 70/2025?
- Key New Provisions Businesses Must Pay Special Attention To
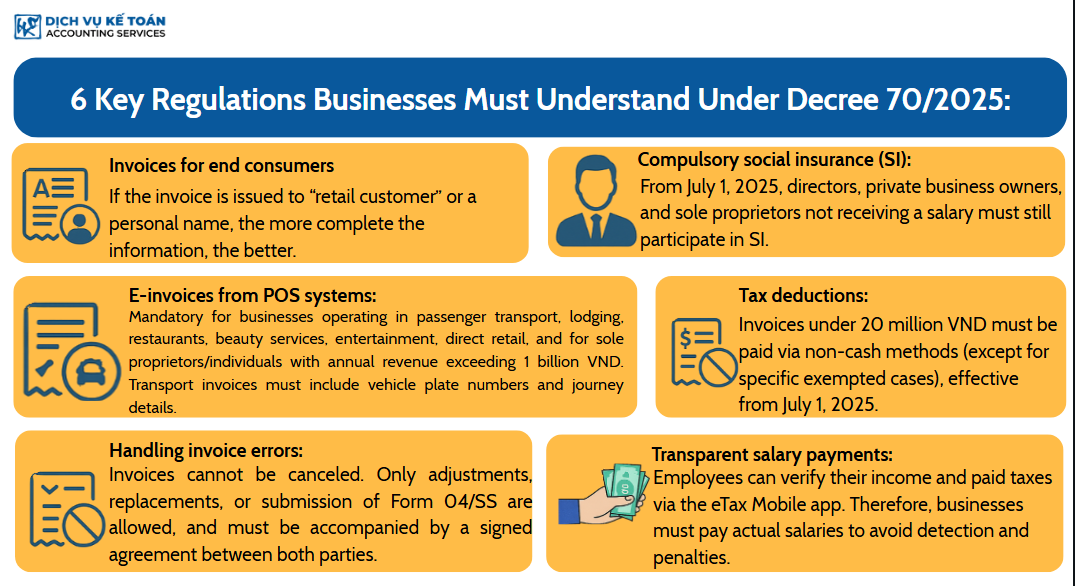
- 1. Businesses selling directly to end consumers must record full buyer information on invoices
- 2. Mandatory use of POS systems for certain service sectors: Transportation, F&B, hotels, etc.
- 3. Invoice errors must be corrected or replaced—not canceled
- 4. Mandatory Social Insurance (SI) for non-salaried business owners (from July 1, 2025)
- 5. Non-cash payments required for all deductible expenses, even under 20 million VND
- 6. Transparent salary & tax reporting via ETAX MOBILE: Actual salaries must be declared
- Impact of Decree 70/2025 on Accounting and Tax Operations
- Common Mistakes and How to Address Them
- Solutions for Effective Compliance with Decree 70/2025
What is Decree 70/2025?
Decree No. 70/2025/ND-CP (hereinafter referred to as “Decree 70/2025”) is a newly promulgated legal regulation issued by the Vietnamese Government. It is considered a breakthrough step in the modernization of tax administration and enhancement of transparency in business activities in Vietnam.
In the context of the Fourth Industrial Revolution and rapid national digital transformation, this Decree not only amends individual provisions but also establishes a comprehensive and stricter legal framework. It focuses on combating invoice fraud, preventing loss of state revenue, and standardizing economic transactions.
At its core, Decree 70/2025 provides detailed regulations for applying information technology in tax management, including the use of e-invoices, point-of-sale systems integrated with the tax authority, and income transparency via mobile applications. Its ultimate goal is to build a system where all transactions by businesses and individuals are recorded accurately, completely, and in a timely manner—fostering a fair, healthy, and well-governed business environment. The Decree is expected to have widespread impact on all aspects of accounting and tax operations across all business types.
Key New Provisions Businesses Must Pay Special Attention To
Decree 70/2025 introduces a series of new provisions that directly affect the day-to-day operations of enterprises. Understanding and complying with these regulations is not only a legal obligation but also critical for avoiding legal risks and unnecessary penalties.
1. Businesses selling directly to end consumers must record full buyer information on invoices
This regulation serves two main purposes. First, it protects consumer rights by ensuring they have valid documents for warranty, complaints, or promotional participation. Second, and more importantly, it prevents businesses from consolidating multiple retail transactions into fake invoices issued to other companies for inflating deductible input costs.
As a result, businesses must revise their sales and payment processes. Cashiers must be trained to accurately collect buyer information, and POS (Point-of-Sale) systems may need upgrades to support fast entry and printing of this data.
2. Mandatory use of POS systems for certain service sectors: Transportation, F&B, hotels, etc.
The critical requirement here is not just the POS machine, but real-time data transmission. Revenue from all transactions must be automatically sent—either in real time or at short intervals—to the tax authority’s system.
This allows tax authorities to monitor revenue directly, combating tax evasion in cash-heavy industries. Affected businesses must invest in qualified POS systems, compatible sales management software, and ensure a stable internet connection.
3. Invoice errors must be corrected or replaced—not canceled
- Adjustment invoice: Used when errors involve values like amounts or tax rates, but key buyer information remains correct. The invoice must state clearly that it is an “increase/decrease adjustment” for the original invoice.
- Replacement invoice: Applied when critical information (buyer’s name, tax code, item names) is incorrect. The replacement must specify the original invoice it replaces, and the original becomes invalid.
- Form 04/SS submission: For errors that are not corrected or replaced, businesses must file Form 04/SS-HĐĐT to explain the error to tax authorities.
Download Form 04/SS here
This creates an auditable trail that cannot be erased, ensuring transparency in all changes. It also requires utmost caution from accountants, as any correction becomes traceable and subject to inspection.
4. Mandatory Social Insurance (SI) for non-salaried business owners (from July 1, 2025)
This regulation significantly affects operating costs for millions of micro, small, and medium enterprises. According to the revised Social Insurance Law effective July 1, 2025, business operators—even those not listed on the payroll or receiving wages—must enroll in SI.
Specifically includes:
- Owners of sole proprietorships
- Directors or General Directors of single-member LLCs owned by individuals
- Registered household business owners
Previously, many avoided payroll inclusion to reduce costs. Now, this “grey area” is eliminated. The intent is to ensure long-term social welfare benefits (pension, sick leave, maternity leave) for business owners and ensure fairness with employees.
Impact on businesses:
- Increased fixed costs: SI contributions must be paid monthly based on income (typically no less than regional minimum wage).
- Declaration and tracking obligations: HR and accounting departments must promptly register, report headcount changes, and handle SI payments to avoid retroactive penalties.
This change demands a new mindset toward cost management, viewing SI contributions as a strategic investment in leadership well-being.
5. Non-cash payments required for all deductible expenses, even under 20 million VND
From July 1, 2025, all business purchases must be settled using non-cash methods to qualify for VAT deduction and corporate income tax expense recognition—regardless of amount.
This aims to push Vietnam toward a fully cashless economy and ensure financial transparency via the banking system. For businesses, this eliminates the use of cash for small transactions with corporate suppliers and requires strict internal payment policies. It may challenge flexibility and speed in some operations.
6. Transparent salary & tax reporting via ETAX MOBILE: Actual salaries must be declared
Employees can now access real-time information about their salaries and withheld PIT (personal income tax) through the Etax Mobile app, using their digital ID (VNEID).
This ends the common “dual payroll” practice (reporting a lower official salary and paying the remainder in cash). With this transparency, businesses are required to declare and pay full actual wages, including corresponding taxes and SI—significantly increasing labor costs.
Impact of Decree 70/2025 on Accounting and Tax Operations
The implementation of Decree 70/2025 forces businesses to reevaluate all accounting and tax workflows, leading to:
- Higher compliance costs: Investments in accounting software, POS systems, SI contributions, and payroll transparency.
- Technology adoption: Manual or semi-automated accounting is no longer viable. Full integration of accounting, sales, banking, and tax systems becomes essential.
- Stricter workflows: All processes—from sales and procurement to payroll—must follow strict, transparent procedures. Mistakes can result in immediate financial penalties.
- Reduced room for evasion: Illegal invoicing, underreporting revenue, or dual payrolls will be harder to conceal due to data integration and real-time monitoring.
- Elevated role for accountants and tax advisors: Accountants must now manage compliance and risk, while expert consultants will be essential for safe navigation and cost optimization.
Common Mistakes and How to Address Them
- Mistake 1: Incomplete retail invoice info
- Penalty: Administrative fines
- Fix: Train sales staff, upgrade POS systems for easy data input
- Mistake 2: Canceling sent e-invoices
- Penalty: Illegal action with potential severe fines
- Fix: Only use adjustment/replacement methods or submit Form 04/SS
- Mistake 3: Failing to register non-salaried directors for SI
- Penalty: Retroactive payments with high interest
- Fix: Immediate registration from July 1, 2025
- Mistake 4: Paying cash for expenses and claiming tax deductions
- Penalty: Rejected deduction, lost VAT refund
- Fix: Enforce non-cash payment policy for all B2B purchases

Solutions for Effective Compliance with Decree 70/2025
- Conduct internal compliance audits: Review all operations against Decree 70 to identify risks and corrective actions.
- Invest in integrated technology: Choose robust software that connects accounting, HR, tax, and sales functions.
- Standardize workflows and retrain teams: Organize regular training and documentation of new procedures.
- Engage professional advisors: Partner with accounting and tax experts for guidance, compliance assurance, and optimization.
Decree 70/2025 represents a comprehensive tax reform initiative in Vietnam. While its early implementation may bring challenges and costs, it paves the way for a more transparent, equitable, and modern business environment.
Businesses that proactively adapt, embed compliance into their culture, and embrace technology will not only survive but gain a strong competitive edge in the digital economy.
For any inquiries, contact Wacontre Accounting Services via Hotline: (028) 3820 1213 or email info@wacontre.com for prompt assistance. With a team of experienced professionals, Wacontre is committed to providing dedicated and efficient service. (For Japanese clients, please contact Hotline: (050) 5534 5505).