The K-factor for managing e-invoice risks is becoming an important tool for tax authorities to control and prevent fraud. Let’s learn about the “K-factor”, “e-invoice risks” and the latest things businesses need to know.
What is the K-Factor in E-Invoice Risk Management?
The K-Factor is an index used to assess the risk level associated with issuing and using e-invoices by businesses. This index is utilized by tax authorities to classify enterprises into different levels of risk, from low to high, thereby enabling more focused and effective tax administration, inspection, and audit.
The K-Factor is periodically calculated by the tax authority’s data system based on various criteria, including tax compliance history, financial status, type of business, and invoicing behavior. Applying the K-Factor enhances the ability of tax authorities to detect risks and tax fraud while allowing compliant businesses to receive administrative privileges.
The Role of the K-Factor in Tax Risk Management
1. How the K-Factor is Applied in Invoice Monitoring
The K-Factor is a behavioral analysis tool that enables tax authorities to identify businesses at risk of violating tax regulations. Enterprises with a low K-Factor are generally subject to less frequent inspections, whereas those with a high K-Factor are closely monitored.
This approach allows tax authorities to allocate resources more effectively by focusing on high-risk entities instead of conducting broad and inefficient inspections. Especially with the nationwide implementation of e-invoicing, the K-Factor helps detect anomalies quickly.
2. Key Criteria Affecting a Business’s K-Factor
Several factors influence the K-Factor, including:
-Tax compliance history
-Timeliness of financial and invoice reporting
-Sudden changes in revenue, profit, or volume of invoices
-Outstanding tax liabilities or administrative violations
-Business type and sector of operation
Each criterion is scored by the risk management system of the tax authority and aggregated into an overall K-Factor rating.
3. Risk Levels and K-Factor Classification
Although not publicly disclosed in detail, the K-Factor is generally classified into three levels:
–Low (K1): Compliant businesses with minimal risk
–Medium (K2): Some indicators require further monitoring
–High (K3): Multiple irregularities with high fraud risk
This classification directly impacts how businesses are supervised and supported by the tax authorities.
Latest Updates on the K-Factor from Tax Authorities
1. Changes in Assessment and Calculation Methods
From 2024 onward, tax authorities began using Big Data analytics and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to update the K-Factor in real time. This advancement enables quicker and more accurate risk detection. The system automatically cross-checks abnormal indicators in tax declarations, invoice use, and cash flow.
Additionally, the assessment criteria for the K-Factor have been expanded to more accurately reflect a company’s financial health and legal compliance.
2. Timeline for Implementation of New Regulations
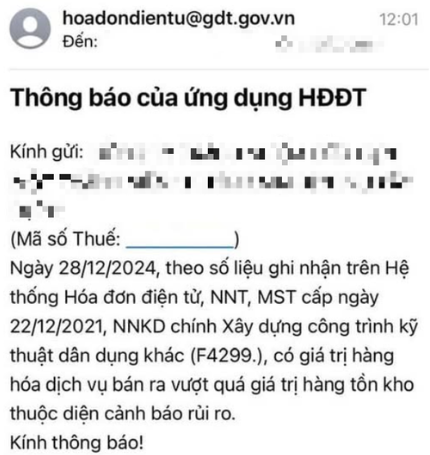
These changes have been in effect since Q2/2024. Businesses identified as high-risk receive electronic alerts through the tax administration system. While these alerts do not carry immediate legal consequences, they serve as a basis for businesses to review and correct their operations.
The tax authority also collaborates with banks and customs departments to gather more comprehensive data for risk assessment.
3. How Businesses Should Prepare to Adapt
Businesses should establish transparent accounting systems and properly archive invoices, while ensuring timely submission of all required reports. Using compliant accounting and e-invoicing software is a key factor in improving the K-Factor.
Moreover, business leaders must stay informed about tax policy updates and strengthen staff training to ensure long-term compliance.
Steps to explain the K coefficient to the tax authority
1. Prepare the explanation documents: need to be clear, complete and convincing.
-Sample letter explaining the K coefficient
-Economic contract, purchase/sale invoice
-Receipt/expenditure voucher, sales list, purchase diary
-Images or videos of the business activities of the enterprise (if necessary)
2. Contact the tax authority and proceed to work:
-After submitting the documents, the tax management officer may invite you to work
-Prepare yourself to explain clearly, provide full evidence
-If necessary, ask the officer to come down to survey the actual business establishment
The K-Factor is more than just a technical metric—it is a critical tool in tax risk management. Enterprises must clearly understand its significance, how it works, and the factors that influence it in order to adjust their operations accordingly. In the era of comprehensive digital transformation in the tax sector, maintaining a favorable K-Factor is essential for businesses to grow sustainably, transparently, and efficiently.
For any inquiries, contact Wacontre Accounting Services via Hotline: (028) 3820 1213 or email info@wacontre.com for prompt assistance. With a team of experienced professionals, Wacontre is committed to providing dedicated and efficient service. (For Japanese clients, please contact Hotline: (050) 5534 5505).
Click register now to get the form here