In the digital age, the need to sign contracts through electronic platforms is becoming increasingly popular. Alongside traditional paper contracts, electronic contracts are a new method that helps businesses save costs, speed up processing, and improve management efficiency. However, many businesses are still concerned about the legal validity and the process of implementing this type of contract. The following article will provide a comprehensive overview of contracts, particularly electronic contracts, according to the latest laws.
What is a contract? What types of contracts are there?
Definition of a contract according to the Civil Code
According to Article 385 of the 2015 Civil Code, a contract is an agreement between the parties to establish, change, or terminate civil rights and obligations. A contract can be expressed orally, in writing, through specific actions, or via electronic means with an electronic signature.
The signing of a contract is an important legal basis to ensure clear rights and obligations between the parties in various fields: labor, commerce, construction, services, civil matters, etc.
Classification of common types of contracts
Contracts can be divided into different categories based on legal criteria or usage purposes, including:
- By form: written contract, oral contract, electronic contract.
- By field: labor contract, civil contract, economic contract, goods sale contract.
- By object: bilateral contract, unilateral contract.
- By enforceability: template contract, negotiated contract.
In the digital age, electronic contracts are increasingly used due to their convenience and effectiveness, especially in e-commerce and logistics.
Legal significance of contracts
A contract serves as legal evidence that clearly defines the rights and obligations between the parties. It helps:
- Reduce the risk of disputes.
- Create a basis for resolution if there is a breach of obligations.
- Serve as a mandatory document when dealing with regulatory authorities, audits, and banks.
The clearer and more complete the contract, the more binding it becomes, and the more it protects the interests of all parties involved.
Essential elements of a valid contract
A valid contract must meet the following conditions (according to Article 117 of the Civil Code):
- The parties must have legal capacity and civil legal capacity.
- The parties must act voluntarily.
- The purpose and content must not violate legal prohibitions or social ethics.
- The contract form must comply with legal regulations (for example, certain contracts must be in writing).
For electronic contracts, the authentication and security elements (such as digital signatures, digital certificates) are essential to ensure legal validity.
Latest updates on contracts
According to the 2023 Electronic Transactions Law (effective from July 1, 2024):
- An electronic contract has the same legal value as a paper contract, provided it meets valid identification and electronic signature requirements.
- The electronic contract storage system must be capable of verifying the origin, signing time, and the integrity of the content.
- The contract signing process can be carried out entirely through digital platforms, as long as security and authentication conditions are met.
These updates create a clear legal framework, encouraging businesses to transition from traditional contracts to more efficient electronic contracts.
What is an Electronic Contract? Does it have legal value?

Definition of an electronic contract under the Electronic Transactions Law
According to Clause 8, Article 3 of the Electronic Transactions Law 2023, an electronic contract is a contract created in the form of a data message, which is generated, sent, received, and stored by electronic means. The signing of the contract is carried out through digital signatures, electronic signatures, or other authentication methods recognized by the law.
An electronic contract can completely replace traditional paper contracts in most civil and commercial transactions today, as long as it meets the legal requirements.
Legal value of electronic contracts
The current law clearly states that: an electronic contract has the same legal value as a written contract if it meets the following conditions:
- There is mutual agreement from all parties involved.
- The parties have legal capacity and civil act capacity.
- The agreement does not violate the law or social ethics.
- The content and format comply with legal regulations and can verify the signature, time, and content.
In other words, an electronic contract can be used as evidence in legal disputes, audits, or tax filings if it is signed according to the proper standards.
Differences between electronic contracts and paper contracts
| Criteria | Paper Contract | Electronic Contract |
| Form | Printed, handwritten | PDF, XML files with electronic signatures |
| Signing | Ink pen, official stamp | Digital signature, OTP, identification code |
| Storage | Physical files | Cloud storage, server |
| Processing Speed | Slow, manual | Fast, remote signing possible |
| Application Scope | All areas | Expanding strongly in e-commerce, logistics, finance… |
Special subjects in electronic contracts
In addition to the typical signing parties, an electronic contract may also include some special subjects such as:
- Organizations providing the platform for contract conclusion (e.g., VNPT, FPT.eContract, TrustSign…).
- Organizations certifying digital signatures (CA).
- Intermediaries storing and verifying data messages.
These subjects play a role in ensuring the security, integrity, and verification of the legal validity of an electronic contract when disputes arise.
Legal regulations governing electronic contracts
Some important documents regulating electronic contracts include:
- The Electronic Transactions Law 2023;
- The Civil Code 2015;
- Decree No. 130/2018/ND-CP on digital signatures;
- Circular No. 01/2021/TT-BTP guiding the conclusion of electronic contracts in civil matters;
- Internal documents on contract management of agencies, organizations, and enterprises.
Companies need to adhere to the correct legal framework when choosing the appropriate method for concluding contracts based on the nature of their activities and legal requirements.
The Standard Process for Signing an Electronic Contract
Agreement and Creation of the Contract on a Digital Platform
The first step in signing an electronic contract is drafting the contract content and agreeing on the terms between the parties. This can be done through email, office software, or directly on an electronic contract platform (e.g., FPT.eContract, VNPT eContract, etc.).
After reaching an agreement, the contract initiator will:
- Upload the contract to the system,
- Provide the details of the parties involved,
- Set the signing sequence and deadline.
The content of the electronic contract must ensure all provisions are included, just like in a traditional paper contract: information about the parties, rights and obligations, payment terms, termination clauses, etc.
Signing with Electronic or Digital Signatures
The contract is signed electronically in the following ways:
- Digital signatures issued by a certification authority (CA),
- Electronic signatures through OTP, QR code, or identity authentication codes,
- Other legally recognized electronic authentication methods under the Electronic Transactions Law.
The contract will only be considered valid once the electronic signature is attached to the document and can be authenticated for identity and signing time.
Storage and Verification of Contract Information
After the contract is signed, it will be stored in the system in a digital format, such as PDF, XML, or encrypted files.
The business must ensure:
- Data is stored in a location where it can be checked and retrieved at any time,
- There is a mechanism to verify the origin, time, and content of the contract,
- The integrity is ensured and cannot be tampered with.
The standard retention period for electronic contracts is typically at least 10 years (especially for financial, accounting, and tax sectors).
Authentication and Data Security Mechanisms
To increase legal validity and protect against legal risks, businesses should use:
- Contract authentication services from trusted platforms,
- Data encryption, multi-layered authentication (OTP, eKYC, etc.),
- Tiered access rights, tracking of access history and actions.
Some organizations also offer timestamping services, which help verify the time the contract was signed and its legal validity.
Handling Rejected or Canceled Contracts
In case one party refuses to sign or wishes to amend the contract:
- The platform will record the status of rejection or postponement,
- The initiator can withdraw, edit, or resend the contract,
- Any actions of cancellation or refusal will be logged in the system for use as evidence in case of a dispute.
The electronic contract signing process is fully carried out on the system, ensuring transparency and clarity at every step of the transaction.
Advantages and Risks of Using Electronic Contracts
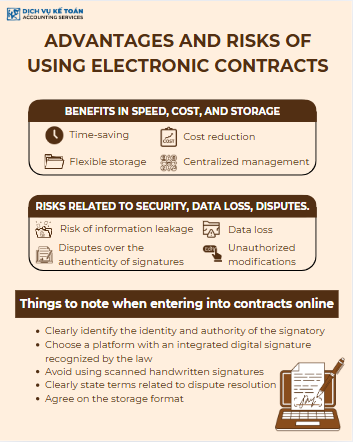
Benefits in Speed, Cost, and Storage
Compared to traditional paper contracts, electronic contracts offer several clear advantages:
- Time-saving: Signing contracts can be completed in minutes without the need for face-to-face meetings.
- Cost reduction: There are no costs for printing, mailing, or express delivery.
- Flexible storage: Contracts are stored on digital platforms, making them easy to search, retrieve, and synchronize with document management software.
- Centralized management: It is easy to monitor the signing process, update the status of each party, and integrate automatic reporting.
These benefits are especially useful in high-speed business environments, such as e-commerce, logistics, and finance, where multi-location transactions are common.
Risks Related to Security, Data Loss, and Disputes
Although convenient, electronic contracts come with potential risks if businesses do not have good security procedures in place:
- Information leakage if the storage system does not encrypt data.
- Data loss due to system errors and lack of regular backup.
- Disputes regarding the authenticity of signatures if scanned images are used instead of proper digital signatures.
- Unauthorized contract modifications if there is no timestamping mechanism or log tracking of changes.
These risks can cause the electronic contract to lose its legal validity and could even lead to the contract being dismissed by the court in case of a dispute.
Role of Third Parties and Certification Entities
A valid electronic contract requires the participation of:
- Contract platform providers (e.g., TrustSign, FPT.eContract, VNPT),
- Digital signature certification organizations (CA), such as Bkav, Viettel-CA, FPT-CA, etc.,
- Third-party intermediaries for storage: Ensuring data backup, security, time-stamping, and clear legal evidence.
These entities ensure transparency, security, and legality throughout the electronic contract signing process.
Considerations When Concluding Contracts Online
When using electronic contracts, businesses should consider:
- Clearly identifying the identity and authority of the signatories,
- Choosing platforms that integrate legally recognized digital signatures,
- Avoiding the use of scanned handwritten signatures, as they do not hold legal value unless verified,
- Clearly stating the provisions regarding dispute resolution through electronic means,
- Agreeing on storage formats (PDF, XML, JSON) that support content integrity checks.
Ways to Mitigate Risks in Electronic Contract Signing
Here are some measures to reduce risks when using electronic contracts:
- Use digital signatures issued by reputable CA organizations,
- Store contracts in systems with multi-layer backup, preventing unauthorized alterations,
- Log all signing activity (access logs, IP addresses, timestamps),
- Use timestamping services,
- Train legal and accounting personnel to understand and manage electronic contracts effectively.
For any inquiries, contact Wacontre Accounting Services via Hotline: (028) 3820 1213 or email info@wacontre.com for prompt assistance. With a team of experienced professionals, Wacontre is committed to providing dedicated and efficient service. (For Japanese clients, please contact Hotline: (050) 5534 5505).








